
Introduction:
In the dynamic landscape of email communication, ensuring the delivery of your messages is crucial. One key element in this realm is the DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM) record. As of 2024, new compliance rules from Gmail and Yahoo highlight the significance of properly setting up DKIM records. This blog post explores the importance of DKIM, the recent compliance updates, and touches upon other essential DNS records like SPF and DMARC.
Understanding DKIM Records:
DKIM is an email authentication method that allows the sender to digitally sign their messages, assuring the recipient that the email has not been tampered with during transit. This cryptographic signature, attached to the email header, provides a mechanism for verifying the legitimacy of the sender.
Importance of DKIM Records:
1. Email Integrity: DKIM ensures that the content of your emails remains intact and unaltered, instilling trust in your recipients.
2. Sender Reputation: Properly configured DKIM records contribute to a positive sender reputation, which is crucial for high deliverability rates.
3. Compliance with Gmail and Yahoo Rules (2024): Gmail and Yahoo have introduced stricter compliance rules, making it mandatory for senders to implement DKIM. Failure to do so might result in emails being marked as spam or rejected altogether.

New 2024 Compliance Rules:
Both Gmail and Yahoo have taken significant steps to enhance email security and combat phishing attempts. As of 2024, emails sent to their platforms must have a valid DKIM signature for authentication. This measure aims to protect users from malicious activities and ensures a safer email environment for all.
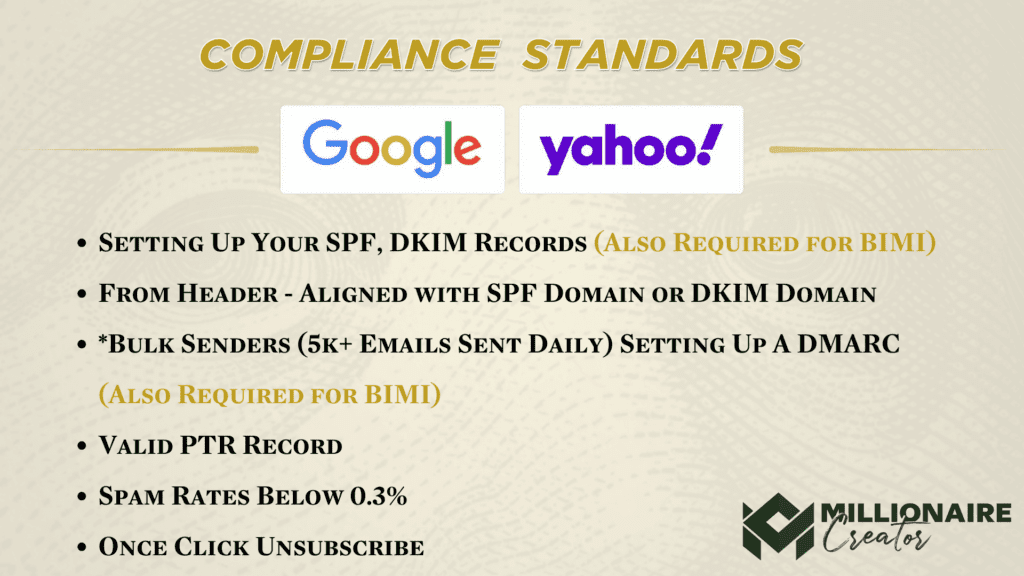
Other Essential DNS Records:
1. SPF (Sender Policy Framework): SPF records define the authorized mail servers for a domain, preventing email spoofing. It complements DKIM by specifying which servers are allowed to send emails on behalf of a domain.
2. DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance): DMARC records provide an additional layer of security by allowing domain owners to specify how email failures should be handled. This includes guidance on what to do if SPF or DKIM checks fail, reducing the risk of phishing attacks.
Setting Up and Configuring DKIM Records:
1. Generate DKIM Keys: Begin by generating a pair of cryptographic keys – a private key kept securely with the sender and a public key published in the DNS records.
2. Configure DNS Records: Add the public key to your DNS records as a TXT record. This step is essential for email servers to retrieve and verify the DKIM signature.
3. Regular Monitoring: Periodically monitor your DKIM configuration to ensure continued compliance with evolving standards and prevent potential deliverability issues.

Verify your email DNS records below:
Conclusion:
As we navigate the evolving landscape of email communication, adapting to the latest compliance rules is key. By prioritizing the setup of DKIM records, you not only adhere to the 2024 guidelines set by Gmail and Yahoo but also reinforce your commitment to secure and trustworthy email communication. Remember, the trio of DKIM, SPF, and DMARC isn’t just a technical requirement; it’s your gateway to a reliable and secure email communication strategy.







